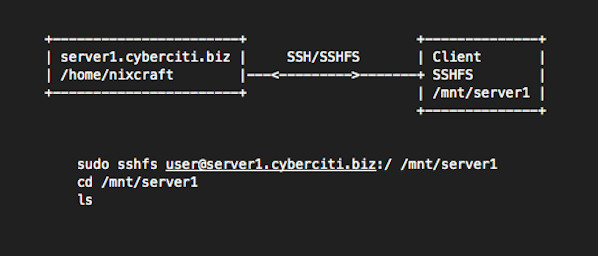
Mounting remote directories over SSH from Windows, Linux and the mac.
I have a Linux server that I like very much. It’s at the hart of my home network and it houses all the data and projects I’m working on. My music collection, the podcasts I’ve downloaded, textfiles and scripts I’m working on and so forth. The downside is that I don’t always have access to…